Audio
Featured Audio Applications - Noise Cancellation
Active noise cancellation (ANC) is a system or technique of applying an anti-noise waveform, which closely matches the shape and frequency of the offending noise waveform, at an angle of precisely 180 degrees out of phase from the noise at the point which they both reach the target area...
ANC systems tend to be small, portable, and adjustable for various environments. They can be effectual across the entire noise spectrum, but especially for low frequencies of up to 300 Hz, where other systems are less effective. For a highly effective ANC system , the noise source must be basically stationary in relation to the speaker emitting the anti-noise waveform. The ANC system should also be located fairly close to the noise source and for best results, the target noise should be mostly broadcasting in one direction.
There are two basic methods used in ANC systems— adaptive cancellation , which uses one or more microphones to detect noise and then adapts to generate an anti-noise waveform; and the synthesis method , which involves sampling and storing a number of noise cycles and generating an anti-noise waveform based on the stored information.
ANC is particularly useful for applications involving industrial equipment, dynamic systems, and domestic appliances. Some ANC systems can tackle the sound cancellation needs of multi-dimensional environments like a working factory. Others function as zone silencing systems which might be used, for example, to cancel the noise around the head of a driver in a vehicle.
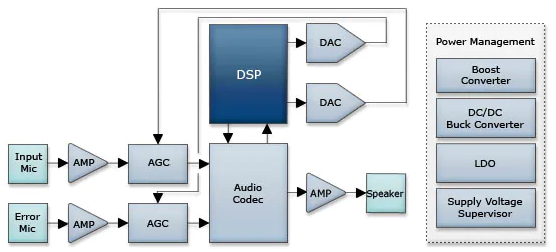
This design is for reference only. The design, as well as the products suggested, has not been tested for compatibility or interoperability.
DSPs for Noise Cancellation
A digital signal processor ( DSP ) is a specialized microprocessor usually with a modified Harvard architecture and a single cycle multiply-and-accumulate required for the fast operational needs of processing and for mathematically manipulating real-world signals like voice, audio, and video. In a noise cancellation application, the DSP examines the characteristics of the input noise waveform. The DSP then generates the anti-noise waveform which effectively negates the input noise waveform. The human ear then hears less "white" noise as the cancellation occurs in real, or near-real time.