Audio
Wireless headphones
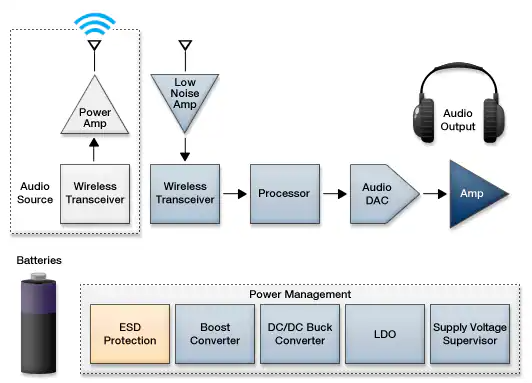
Wireless headphones contain small speakers, receive signals via a short-distance transmission link, and typically operate on a battery to enable users to work without the hassle of a cord inhibiting movement and productivity. Wireless technology replaces physical cabling where it is inconvenient, dangerous, or impossible to use cables or wires...
Wireless headphones have the option to use several different wireless transmission technologies such as FM, Bluetooth, and Wi-Fi. Wireless headphones are also a useful, though not essential, option for remote monitoring, CD/DVD players, home theater, personal computers, portable devices such as digital/mp3 players and mobile phones; and disc jockeying, sound engineering and military functions, to name a few.
Two major methods of transmission for wireless headphones are IF (Infrared) and RF (Radio Frequency). Both types of wireless technology implement a transmitter and receiver system. The transmitter connects to the audio source while the receiver is built-in to the wireless headphones, accepting incoming signals and handing off the signal for processing in the signal chain until it reaches the speakers to create sound for only your ears to hear.
Wireless headphones can also be separated into three categories depending on how they interact with the ear. Circumaural headphones or full size headphones have circular earpads that completely surround the ear and can be designed to form a full seal against the head to decrease unwanted external noise. Supra-aural headphones have pads that sit on the ears instead of around them, and tend to be smaller and lighter than circumaural headphones, thus providing less reduction of outside noise. And the last type is earbuds or earphones, which are much smaller, are placed directly outside the ear canal without fully covering it, and are often favored for their general low cost, small size, portability, and convenience.
Headphone Amplifier for Wireless Headphones
Headphone amplifiers have specifications tuned for driving headphone speakers. Amplifiers have enormous voltage gain, use feedback to operate, and can be classified in different ways. They can be identified by the device they are intended to drive (e.g., headphone amplifier, speaker amplifier), the input that they are to amplify (e.g. guitar amplifier), the frequency range of the signal (e.g., RF, Audio), and by the function that they perform (e.g. inverting amplifier, power amplifier.)
Application Notes and Resources
- Wireless Audio - ST
- Wireless Headset - ON Semi
- Wireless Headset - TI
- Gaming Headset - Freescale
- Headsets - Wolfson